| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 상속
- Database
- spring
- Array
- MVC
- Thymeleaf
- 이클립스
- JDBC
- string
- Eclipse
- Controller
- mysql
- jquery
- View
- Oracle
- db
- git
- React
- Scanner
- 배열
- rpa
- 문자열
- Java
- API
- SpringBoot
- Uipath
- 조건문
- jsp
- html
- Board
- Today
- Total
유정잉
52일차 스프링 [ Component, AOP, JDBC ] 본문
[ Component2 - project ]
1) Test, Test2, Test3, Test4, Test5
@Component로 설정하고 이름도 설정할수 있음 (=@Component("이름"))
@Lazy의 객체 생성 시점 : getBean 메서드를 호출할 때 객체가 생성된다
@Scope("prototype") : 프로토타입 scope는 싱글톤 scope과 달리 IoC에서 빈을 받아올때마다 매번 인스턴스를 새로 생성한다.
@PostConstruct : 생성자 호출 이후 자동으로 호출될 메서드
@PreDestroy : 객체 소멸될 때 자동으로 호출 될 메서드
package beans;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Test {
public Test() {
System.out.println("Test 생성자");
}
}package beans;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("component2")
public class Test2 {
public Test2() {
System.out.println("Test2 생성자");
}
}package beans;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Lazy //객체 생성 시점 : getBean 메서드 호출할때 객체가 생성된다
public class Test3 {
public Test3() {
System.out.println("Test3 생성자");
}
}package beans;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
public class Test4 {
public Test4() {
System.out.println("Test4 생성자");
}
}package beans;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Lazy
public class Test5 {
public Test5() {
System.out.println("Test5 생성자");
}
@PostConstruct //생성자 호출 이후 자동으로 호출될 메서드
public void init() {
System.out.println("init");
}
@PreDestroy //객체 소멸될 때 자동으로 호출될 메서드
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy");
}
}
2) BeanClass.java
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans")
package config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import beans.Test2;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans")
public class BeanClass {
@Bean
public Test2 t2() { //Test2는 이름이 있는 Bean이여서 이름을 바꿔주고 싶어서 적어줌 !
return new Test2();
}
}
3) MainClass에서 출력
package main;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import beans.Test;
import beans.Test2;
import beans.Test3;
import beans.Test4;
import beans.Test5;
import config.BeanClass;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
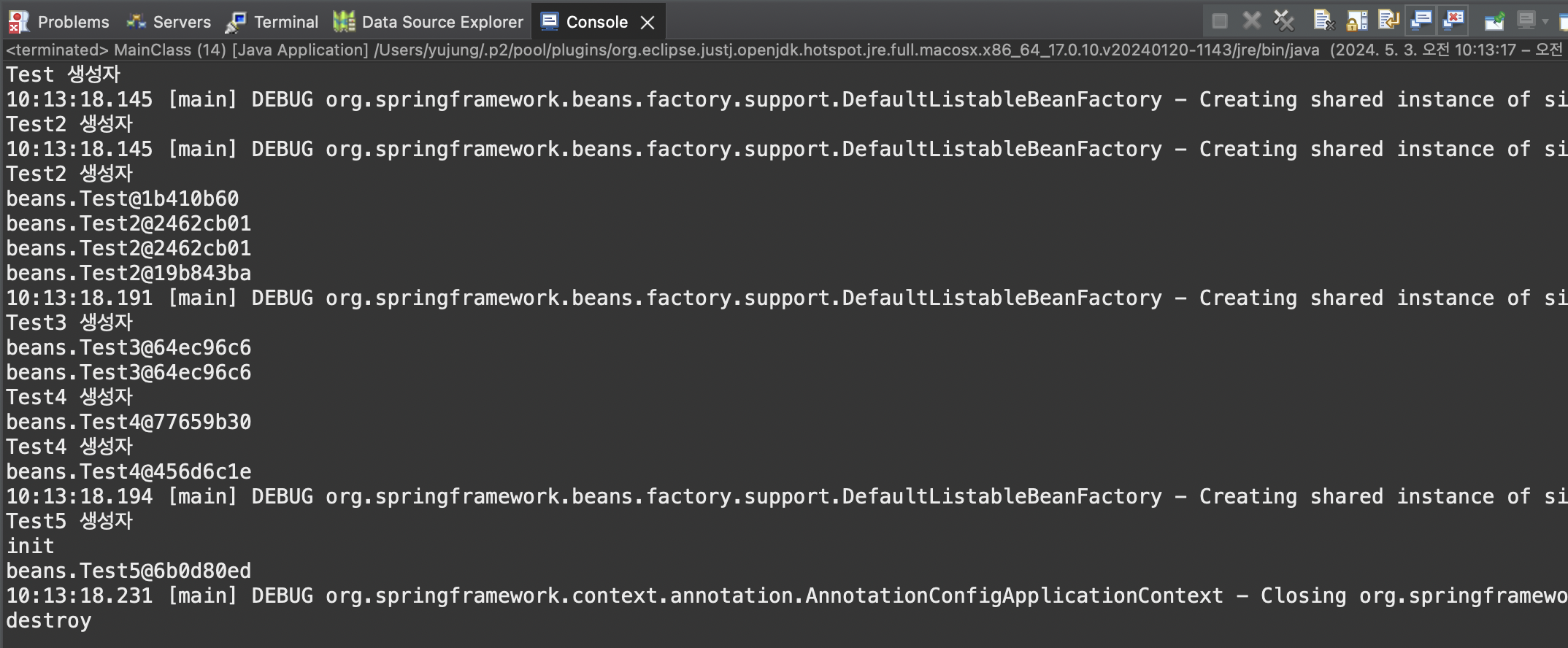
//이 코드만 작성하고 BeanClass를 로딩할 때 생성되는 것이므로 생성자만 출력 됨 Main에서 로딩을 하자마자 기본생성자 호출 됨
//근데 Test3 , 4 는 Scope Lazy가 있어서 호출 되지 않음 ! Test와 Test2만 호출 됨 !
//Test에서 한번 객체 등록, Test2에서 한번 객체 등록, BeanClass에서 Test2 객체 한번 등록 -> 총 Test 1 + Test2 = 3개 출력 됨
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanClass.class);
Test t1 = ctx.getBean(Test.class);
System.out.println(t1);
Test2 t2 = ctx.getBean("component2", Test2.class); //ID값(="component2")을 이름(Test2의 @Component("component2"))이랑 똑같이 줬음
System.out.println(t2); //t2과 t22는 싱글톤 객체
Test2 t22 = ctx.getBean("component2", Test2.class);
System.out.println(t22);
Test2 t222 = ctx.getBean("t2", Test2.class); //ID값을 BeanClass의 public Test2 t2()랑 똑같이 줬음
System.out.println(t222); //t2와 t22는 싱글톤 객체 vs t222는 객체의 주소값이 달라짐
Test3 t3 = ctx.getBean(Test3.class);
System.out.println(t3); //t3와 t33는 싱글톤 객체
Test3 t33 = ctx.getBean(Test3.class);
System.out.println(t33);
Test4 t4 = ctx.getBean(Test4.class);
System.out.println(t4); //t4와 t4는 @Scope로 설정해서 싱글톤 객체가 아님
Test4 t44 = ctx.getBean(Test4.class);
System.out.println(t44);
Test5 t5 = ctx.getBean(Test5.class);
System.out.println(t5); //init, PreDestroy
ctx.close();
}
}
4) java 파일에 bean을 등록했기 때문에 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 클래스 사용 !
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanClass.class);
//이 코드만 작성하고 BeanClass를 로딩할 때 생성되는 것이므로 생성자만 출력 됨 Main에서 로딩을 하자마자 기본생성자 호출 됨
//근데 Test3 , 4 는 Scope Lazy가 있어서 호출 되지 않음 ! Test와 Test2만 호출 됨 !
//Test에서 한번 객체 등록, Test2에서 한번 객체 등록, BeanClass에서 Test2 객체 한번 등록 -> 총 Test 1 + Test2 = 3개 출력 됨
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanClass.class);
BeanClass.java (Test는 위에 보면 됨)
package config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import beans.Test2;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans")
public class BeanClass {
@Bean
public Test2 t2() { //Test2는 이름이 있는 Bean이여서 이름을 바꿔주고 싶어서 적어줌 !
return new Test2();
}
}
[ Component3 - project ]

1) Data, Data2, Data3, Data4, Data5
@Component = Bean 등록(bean으로 등록하지 않으면 스프링 환경에서 객체를 사용할 수 없음)
/ Data2 3만 @Component("이름등록")
package beans;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Data {
}package beans;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("component2")
public class Data2 {
}package beans;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("component3")
public class Data3 {
}package beans;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Data4 {
}package beans;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Data5 {
}
2) Test.java 파잂
@Autowired 자동주입 : 외부에 있는 객체를 자동으로 객체 주소값 가져오기(=유지보수쉬워짐, 약한결합성, 효율성증가)
@Qualifier("이름") -> Data2에서 @Component("이름")에 설정한 "이름"값이랑 같게 설정 : 이름 같은 Component를 찾아 d2에 자동 주입
@Resource(name="이름") : @Autowired + @Qualifier("이름") 이 합쳐진 효과 !
만약에 여기서 Data3에 @Component("이름")설정을 안 했지만 Test에서 사용하고 싶을 경우 -> BenaClass에서 bean을 메서드 형식으로(클래스형식은 이미 존재하므로) 등록하고 사용하면 된다
[ Data3 파일 ]
@Component("component3")
public class Data3 {
}
[ Test.java 파일 ]
@Resource(name="component3") //@Autowired+@Qualifier("이름")=@Resource
private Data3 d3;
//Data3에 "component3"은 존재하지만 "component4와 5"는 존재하지 않음 => 즉, 클래스 단위는 이미 존재하므로 메서드 단위로 bean을 새로 생성해야 함
@Resource(name="component4")
private Data3 d4;
@Resource(name="component5")
private Data3 d5;
[ BeanClass.java 파일 ]
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans")
public class BeanClass {
@Bean
public Data3 component4() {
return new Data3();
}
@Bean
public Data3component5() {
return new Data3();
}
}
package beans;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Test {
@Autowired //자동주입 (외부에 있는 객체 자동으로 객체 주소값 가져오기=유지보수쉬워짐, 약한결합성, 효율증가)
private Data d1;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("component2") //Data2에서 이름같은 @Component를 찾아 d2에 자동 주입
private Data2 d2;
@Resource(name="component3") //@Autowired+@Qualifier("이름")=@Resource
private Data3 d3;
//Data3에 "component3"은 존재하지만 "component4와 5"는 존재하지 않음 => 즉, 클래스 단위는 이미 존재하므로 메서드 단위로 bean을 새로 생성해야 함
@Resource(name="component4")
private Data3 d4;
@Resource(name="component5")
private Data3 d5;
public Data getD1() {
return d1;
}
public void setD1(Data d1) {
this.d1 = d1;
}
public Data2 getD2() {
return d2;
}
public void setD2(Data2 d2) {
this.d2 = d2;
}
public Data3 getD3() {
return d3;
}
public void setD3(Data3 d3) {
this.d3 = d3;
}
public Data3 getD4() {
return d4;
}
public void setD4(Data3 d4) {
this.d4 = d4;
}
public Data3 getD5() {
return d5;
}
public void setD5(Data3 d5) {
this.d5 = d5;
}
}
4) BeanClass 파일
package config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import beans.Data3;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans")
public class BeanClass {
@Bean
public Data3 component4() {
return new Data3();
}
@Bean
public Data3 component5() {
return new Data3();
}
}
5) MainClass 출력
package main;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import beans.Test;
import config.BeanClass;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanClass.class);
Test t1 = ctx.getBean(Test.class);
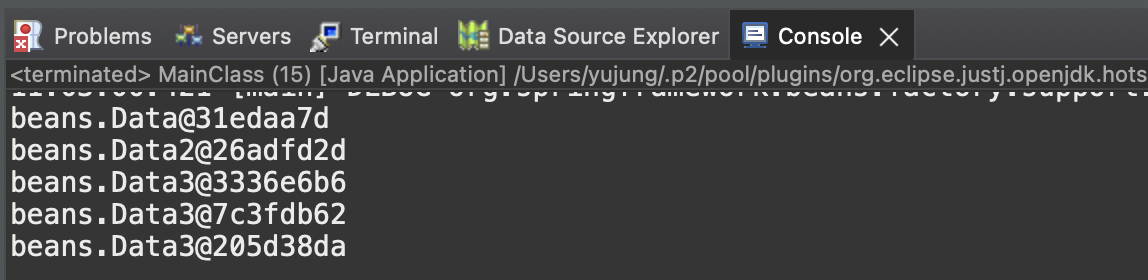
System.out.println(t1.getD1()); //D1~D5각자 다른 주소값 출력
System.out.println(t1.getD2());
System.out.println(t1.getD3());
System.out.println(t1.getD4());
System.out.println(t1.getD5());
}
}
6) Test2.java 파일
@Component
public class Test2 {
private int d1;
private String d2;
private Data4 d3;
private Data5 d4;
//기본생성자의 매개변수 값 변경하는 법 : @Value로 값 넣어주기
public Test2(@Value("1") int d1, @Value("spring") String d2, Data4 d3, Data5 d4) {
this.d1=d1;
this.d2=d2;
this.d3=d3;
this.d4=d4;
}
package beans;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Test2 {
private int d1;
private String d2;
private Data4 d3;
private Data5 d4;
//기본생성자의 매개변수 변경 @Value()로 값을 넣어 줌 !
public Test2(@Value("1") int d1, @Value("spring") String d2, Data4 d3, Data5 d4) {
this.d1=d1;
this.d2=d2;
this.d3=d3;
this.d4=d4;
}
public int getD1() {
return d1;
}
public void setD1(int d1) {
this.d1 = d1;
}
public String getD2() {
return d2;
}
public void setD2(String d2) {
this.d2 = d2;
}
public Data4 getD3() {
return d3;
}
public void setD3(Data4 d3) {
this.d3 = d3;
}
public Data5 getD4() {
return d4;
}
public void setD4(Data5 d4) {
this.d4 = d4;
}
}
7) MainClass 파일
package main;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import beans.Test;
import beans.Test2;
import config.BeanClass;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanClass.class);
Test2 t2 = ctx.getBean(Test2.class);
System.out.println(t2.getD1());
System.out.println(t2.getD2());
System.out.println(t2.getD3());
System.out.println(t2.getD4());
}
}
8) Test3.java 파일
package beans;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Test3 {
private int d1;
private String d2;
private Data4 d3;
private Data5 d4;
// 기본생성자의 매개변수 값 변경하는 법 : @Value로 값 넣어주기
public Test3(@Value("1") int d1, @Value("spring") String d2, Data4 d3, Data5 d4) {
this.d1 = d1;
this.d2 = d2;
this.d3 = d3;
this.d4 = d4;
}
public int getD1() {
return d1;
}
public void setD1(int d1) {
this.d1 = d1;
}
public String getD2() {
return d2;
}
public void setD2(String d2) {
this.d2 = d2;
}
public Data4 getD3() {
return d3;
}
public void setD3(Data4 d3) {
this.d3 = d3;
}
public Data5 getD4() {
return d4;
}
public void setD4(Data5 d4) {
this.d4 = d4;
}
}
9) BeanClass.java 파일
package config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import beans.Data3;
import beans.Data4;
import beans.Data5;
import beans.Test3;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans")
public class BeanClass {
@Bean
public Test3 t3() {
Test3 t3 = new Test3(100, "java", new Data4(), new Data5());
return t3;
}
}
10) MainClass 파일
package main;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import beans.Test;
import beans.Test2;
import beans.Test3;
import config.BeanClass;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanClass.class);
Test3 t3 = ctx.getBean("t3", Test3.class);
System.out.println(t3.getD1());
System.out.println(t3.getD2());
System.out.println(t3.getD3());
System.out.println(t3.getD4());
}
}
11) 최종 결론
package config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import beans.Data3;
import beans.Data4;
import beans.Data5;
import beans.Test3;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "beans")
public class BeanClass {
@Bean
public Data3 component4() {
return new Data3();
}
@Bean
public Data3 component5() {
return new Data3();
}
@Bean
public Test3 t3() {
Test3 t3 = new Test3(100, "java", new Data4(), new Data5());
return t3;
}
}package main;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import beans.Test;
import beans.Test2;
import beans.Test3;
import config.BeanClass;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanClass.class);
Test t1 = ctx.getBean(Test.class);
System.out.println(t1.getD1()); //D1~D5각자 다른 주소값 출력
System.out.println(t1.getD2());
System.out.println(t1.getD3());
System.out.println(t1.getD4());
System.out.println(t1.getD5());
Test2 t2 = ctx.getBean(Test2.class);
System.out.println(t2.getD1());
System.out.println(t2.getD2());
System.out.println(t2.getD3());
System.out.println(t2.getD4());
Test3 t3 = ctx.getBean("t3", Test3.class);
System.out.println(t3.getD1());
System.out.println(t3.getD2());
System.out.println(t3.getD3());
System.out.println(t3.getD4());
}
}
[ AOP- project ]
File - New - Maven Project -> Create a simple project 체크 후 Next -> Grou Id(=kr.bit) Artifact Id(=AOP)
1) beans.xml에 새로운 코드 추가 ( aop 코드 추가 됨 )
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- aop 추가 됨 -->
</beans>
2) pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>kr.bit</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring1</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- xml에서 사용할 속성들 -->
<properties>
<!-- 자바 버전 -->
<java-version>1.8</java-version>
<!-- 스프링 버전 -->
<org.springframework-version>6.0.11</org.springframework-version>
<!--<org.springframework-version>4.3.25.RELEASE</org.springframework-version> -->
<org.slf4j-version>1.7.26</org.slf4j-version>
<ch.qos.logback-version>1.2.3</ch.qos.logback-version>
</properties>
<!-- 프로젝트에서 사용할 라이브러리 정보 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- spring context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- logback -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>${ch.qos.logback-version}</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.annotation/javax.annotation-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.19</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver/1.9.19
이때 <scope>runtime</scope> 이부분은 지워주기 -> 에러 발생할 수도 있음 !!!
3) AdvisorClass
package kr.bit.advisor;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
public class AdvisorClass {
public void beforeMethod() {
System.out.println("before");
}
public void afterMethod() {
System.out.println("after");
}
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pj) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around1");
Object obj = pj.proceed(); //비즈니스메서드 호출 전
System.out.println("around2");
return obj;
}
public void afterReturningMethod() {
System.out.println("afterReturn");
}
}
4) Test
package kr.bit.beans;
public class Test {
public int test() {
System.out.println("test");
return 10;
}
}
5) beans.xml에 aop 환경설정 하기
AdvisorClass와 Test에 함수를 구현하고 beans.xml에 와서 객체 등록 해주는 작업
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- aop 추가 됨 -->
<bean id="test1" class="kr.bit.beans.Test"></bean>
<bean id="advisor1" class="kr.bit.advisor.AdvisorClass"></bean>
<aop:config> <!-- aop에 환경설정 -->
<aop:aspect ref="advisor1">
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* test())" id="point1"></aop:pointcut>
<aop:before method="beforeMethod" pointcut-ref="pont1"/>
<aop:after method="afterMethod" pointcut-ref="point1"/>
<aop:around method="aroundMethod" pointcut-ref="ponit1"/>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturningMethod" pointcut-ref="point1"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
6) MainClass
package kr.bit.main;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import kr.bit.beans.Test;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("kr/bit/config/beans.xml");
Test t1 = ctx.getBean("test1", Test.class);
int n = t1.test();
System.out.println(n);
ctx.close();
}
}
[ AOP2 - project ]
1) AdvisorClass
package kr.bit.advisor;
public class AdvisorClass {
public void beforeMethod() {
System.out.println("before");
}
}
2) kr.bit.beans의 Test , Test2
package kr.bit.beans;
public class Test {
public void m1() {
System.out.println("m1");
}
//weaving
public void m1(int n1) {
System.out.println("int m1");
}
public void m1(String n1) {
System.out.println("String m1");
}
public void m1(int n1, int n2) {
System.out.println("int, int");
}
public void m1(int n1, String n2) {
System.out.println("int, String");
}
public void m2() {
System.out.println("m2");
}
public int m3() {
System.out.println("m3");
return 1;
}
}package kr.bit.beans;
public class Test2 {
public void m1() {
System.out.println("m2");
}
}
3) kr.bit.beans2의 Test
package kr.bit.beans2;
public class Test {
public void m1() {
System.out.println("m1");
}
}
4) beans.xml
expression="execution(void kr.bit.beans.Test.m1(*) -> 모든 매개변수
expression="execution(void kr.bit.beans.Test.m1(*,*) ->모든 매개변수 2개일 경우
expression="execution(void *.*(..) -> 모든 패키지 모든 함수(반환형은 적어줘야함)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- aop 추가 됨 -->
<bean id="advisor1" class="kr.bit.advisor.AdvisorClass"></bean>
<bean id="test1" class="kr.bit.beans.Test"></bean>
<bean id="test2" class="kr.bit.beans.Test2"></bean>
<bean id="test22" class="kr.bit.beans2.Test"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="advisor1">
<!-- <aop:pointcut expression="execution(void kr.bit.beans.Test.m1())" id="p1"></aop:pointcut> -->
<!-- <aop:pointcut expression="execution(void kr.bit.beans.Test.m1(int))" id="p1"></aop:pointcut> -->
<!-- <aop:pointcut expression="execution(void kr.bit.beans.Test.m1(*))" id="p1"></aop:pointcut> -->
<!-- <aop:pointcut expression="execution(void kr.bit.beans.Test.m1(*,*))" id="p1"></aop:pointcut> -->
<!-- <aop:pointcut expression="execution(void kr.bit.beans.*.m1(..))" id="p1"></aop:pointcut> -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(void *.*(..))" id="p1"></aop:pointcut> <!-- 반환형은 적고 모든 패키지 모든 함수 -->
<aop:before method="beforeMethod" pointcut-ref="p1"></aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
5) MainClass
package kr.bit.main;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import kr.bit.beans.Test;
import kr.bit.beans.Test2;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("kr/bit/config/beans.xml");
Test t1=ctx.getBean("test1", Test.class);
t1.m1();
t1.m1(10); //int값 출력
t1.m1("spring");
t1.m1(10,20);
t1.m1(2,"java");
Test2 t2=ctx.getBean("test2", Test2.class);
t2.m1();
}
}
[ AOP3 - project ]
1) AdvisorClass , AdvisorClass2
package kr.bit.advisor;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect //advisor역할을 할 bean설정
@Component
@Order(1)
public class AdvisorClass {
@Before("execution(* m1())")
public void test1() {
System.out.println("before");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* m1())")
public void test2() {
System.out.println("return");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* m1())")
public void test3() {
System.out.println("throw");
}
}package kr.bit.advisor;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect //advisor역할을 할 bean설정
@Component
@Order(1)
public class AdvisorClass2 {
@Around("execution(* m1())")
public Object test1(ProceedingJoinPoint pj) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around one");
Object obj = pj.proceed();
System.out.println("around two");
return obj;
}
@After("execution(* m1())")
public void test2() {
System.out.println("after");
}
}
2) Test
package kr.bit.beans;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Test {
public void m1() {
System.out.println("m1");
}
}
3) beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- aop 추가 됨 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="kr.bit.advisor"></context:component-scan>
<context:component-scan base-package="kr.bit.beans"></context:component-scan>
<!-- advisor 역할을 할 @Aspect 확인해서 Bean 설정 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
4) MainClass
package kr.bit.main;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import kr.bit.beans.Test;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("kr/bit/config/beans.xml");
Test t = ctx.getBean(Test.class);
t.m1();
}
}
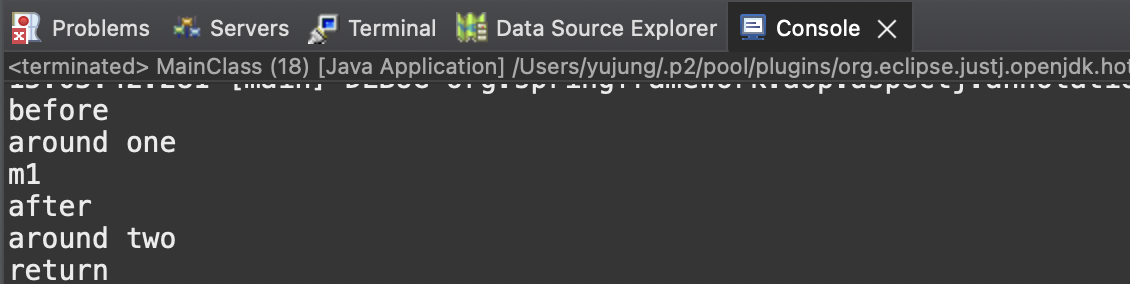
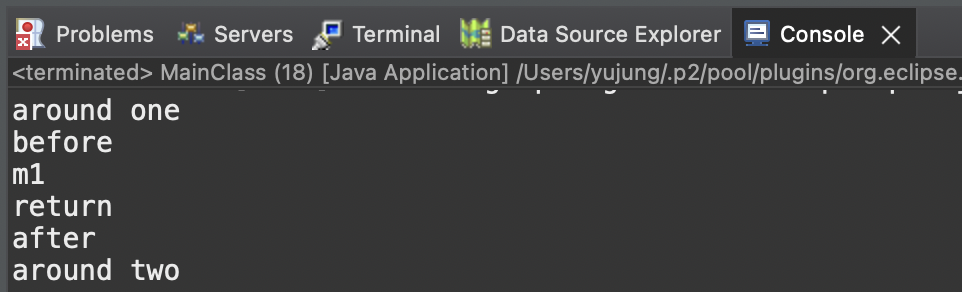
▷ AdvisorClass의 @Order(1), @Order(2)에 따른 출력 결과
5) Beans.java에서 환경 설정(?)
@ComponentScan(basePackages = ({ "" , "" }) => package가 두개 이상일 경우 중괄호 { } 사용하여 표현함
package kr.bit.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"kr.bit.advisor", "kr.bit.beans"}) //두개일때는 중괄호{"",""} 이용해서 적어주기
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class Beans {
}
6) MainClass AnnotationConfigApplicationContext로 출력
package kr.bit.main;
import java.beans.Beans;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import kr.bit.beans.Test;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx2 = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Beans.class);
Test t2 = ctx2.getBean(Test.class);
t2.m1();
}
}
[ Spring_JDBC - project ]
DB 설정시
BasicDataSource
Jdbc
-----------------------
File - New - Maven Project -> Create a simple project 체크 후 Next -> Group Id(=kr.bit) Artifact Id(=Spring_JDBC)

1) pom.xml에 JDBC연결 작업 라이브러리 넣어 주기 !
이때 <repositories>정보도 넣어 줘야 함 !
[ Repository 정보 ]
<!-- Repository 정보 -->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>mysql</id>
<name>MySQL JDBC Repository</name>
<url>URL_TO_MYSQL_REPOSITORY</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
[ Spring JDBC ]
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.11</version> <!-- <version>${org.springframework-version}</version> 두가지 버전 다 가능 -->
</dependency>
[ mysql-conector ]
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.27</version>
</dependency>
[ Apache Commons DBCP ]
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
<version>${org.apache.commons-version}</version>
</dependency>
이때 <version>은 보통 위에 <properties>안에 이런식으로 넣어줌
<org.apache.commons-version>2.7.0</org.apache.commons-version>
그리고 <dependency>안에 <version>에는 태그명 넣어줌
<version>${org.apache.commons-version}</version>
[ MyBatis ]
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</dependency>
[ MyBatis Spring ]
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>kr.bit</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring1</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- xml에서 사용할 속성들 -->
<properties>
<!-- 자바 버전 -->
<java-version>1.8</java-version>
<!-- 스프링 버전 -->
<org.springframework-version>6.0.11</org.springframework-version>
<!--<org.springframework-version>4.3.25.RELEASE</org.springframework-version> -->
<org.slf4j-version>1.7.26</org.slf4j-version>
<ch.qos.logback-version>1.2.3</ch.qos.logback-version>
<org.apache.commons-version>2.7.0</org.apache.commons-version>
</properties>
<!-- Repository 정보 -->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>mysql</id>
<name>MySQL JDBC Repository</name>
<url>URL_TO_MYSQL_REPOSITORY</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<!-- 프로젝트에서 사용할 라이브러리 정보 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- spring context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- logback -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>${ch.qos.logback-version}</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.annotation/javax.annotation-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.19</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.11</version> <!-- <version>${org.springframework-version}</version> 두가지 버전 다 가능 -->
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.27</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.commons/commons-dbcp2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
<version>${org.apache.commons-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis-spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2) MySQL 실행 -> table 생성
create table spring_table(
num1 int,
str1 varchar(10));
3) JBean에서 필드 선언 , Getter&Setter 생성 , @Component Bean 등록 , @Scope
package kr.bit.beans;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
public class JBean {
private int num1;
private String str1 ;
public int getNum1() {
return num1;
}
public void setNum1(int num1) {
this.num1 = num1;
}
public String getStr1() {
return str1;
}
public void setStr1(String str1) {
this.str1 = str1;
}
}
4) Beans에서 JDBC 연결 작업
package kr.bit.config;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import kr.bit.db.MapperInterface;
//이 방법은 java로 환경설정 하는 방법 만약에 xml로 환경설정할 경우 다르게 해야함
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "kr/bit/beans")
public class Beans {
@Bean
public BasicDataSource dataSource() {
BasicDataSource source = new BasicDataSource();
source.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
source.setUrl("jdbc:myslq://localhost:3306/yujung");
source.setUsername("root");
source.setPassword("00000000");
return source;
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory factory(BasicDataSource source) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean fac = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
fac.setDataSource(source);
SqlSessionFactory fac2=fac.getObject();
return fac2;
}
@Bean
public MapperFactoryBean<MapperInterface> test(SqlSessionFactory fac) throws Exception{
MapperFactoryBean<MapperInterface> mapper = new MapperFactoryBean<MapperInterface>(MapperInterface.class);
mapper.setSqlSessionFactory(fac);
return mapper;
}
}
5) MapperInterface의 Interface 파일에 쿼리문 작성
변수 앞에 # 붙이기 #{num1}
package kr.bit.db;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
import kr.bit.beans.JBean;
public interface MapperInterface {
@Select("select num1, str1 from spring_table")
List<JBean> read();
@Insert("insert into spring_table(num1, str1) values (#{num1}, #{str1})")
void in(JBean bean);
@Update("update spring_table set str1=#{str1} where num1=#{num1}")
void up(JBean bean);
@Delete("delete from spring_table where num1=#{num1}")
void del(int num1);
}
6) MainClass AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 사용
package kr.bit.main;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import kr.bit.beans.JBean;
import kr.bit.config.Beans;
import kr.bit.db.MapperInterface;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Beans.class);
MapperInterface m = ctx.getBean("test", MapperInterface.class);
JBean b1 = new JBean();
b1.setNum1(10);
b1.setStr1("str1");
m.in(b1);
JBean b2 = new JBean();
b2.setNum1(20);
b2.setStr1("str2");
m.in(b2);
List<JBean> li = m.read();
for(JBean j:li) {
System.out.println(j.getNum1());
System.out.println(j.getStr1());
}
}
}

[ Spring2_JDBC - project ]

1) pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>co.jw.sol</groupId>
<artifactId>AOP</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- xml에서 사용할 속성들 -->
<properties>
<!-- 자바 버전 -->
<java-version>1.8</java-version>
<!-- 스프링 버전 -->
<org.springframework-version>5.1.9.RELEASE</org.springframework-version>
<!--<org.springframework-version>4.3.25.RELEASE</org.springframework-version> -->
<org.slf4j-version>1.7.26</org.slf4j-version>
<ch.qos.logback-version>1.2.3</ch.qos.logback-version>
<javax.annotation-version>1.3.2</javax.annotation-version>
<org.aspectj-version>1.9.4</org.aspectj-version>
<com.oracle-version>11.2.0.3</com.oracle-version>
<org.apache.commons-version>2.7.0</org.apache.commons-version>
<org.mybatis-version>3.5.6</org.mybatis-version>
</properties>
<!-- Repository 정보 -->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>mysql</id>
<name>MySQL JDBC Repository</name>
<url>URL_TO_MYSQL_REPOSITORY</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<!-- 프로젝트에서 사용할 라이브러리 정보 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- spring context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${org.slf4j-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- logback -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>${ch.qos.logback-version}</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.annotation/javax.annotation-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>${javax.annotation-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>${org.aspectj-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${org.springframework-version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.24</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.commons/commons-dbcp2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId>
<version>${org.apache.commons-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>${org.mybatis-version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis-spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2) beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="test2" class="beans.Test"></bean>
</beans>
3) JBean
package co.jw.sol.beans;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Scope("prototype")
public class JBean {
private int num1;
private String str1;
public int getNum1() {
return num1;
}
public void setNum1(int num1) {
this.num1 = num1;
}
public String getStr1() {
return str1;
}
public void setStr1(String str1) {
this.str1 = str1;
}
}
4) BBean
package co.jw.sol.config;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"co.jw.sol.beans", "co.jw.sol.db"})
public class BBean {
@Bean
public BasicDataSource source() {
BasicDataSource source=new BasicDataSource();
source.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
source.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yujung");
source.setUsername("root");
source.setPassword("00000000");
return source;
}
//DB에 접속해 쿼리를 전달하는 빈을 등록해야함
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate db(BasicDataSource source) {
JdbcTemplate db=new JdbcTemplate(source);
return db;
}
}
5) JdbcDAO
package co.jw.sol.db;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import co.jw.sol.beans.JBean;
@Component
public class JdbcDAO {
//JDBC 관리를 해주는 객체를 주입받고 있다. (BBean.java에서 돌려받은 객체의 주소값을
// db에 넣고있다 -> 타입 기준)
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate db;
//MapperClass 자동주입
@Autowired
private MapperClass mapper;
public void in_sert(JBean bean) {
String sql="insert into spring_table(num1,str1) values(?,?)";
db.update(sql,bean.getNum1(),bean.getStr1());
}
public List<JBean> sel_ect(){
String sql="select num1,str1 from spring_table";
List<JBean> li=db.query(sql,mapper);
//아까 테이블로 부터 값을 꺼내서 bean에 저장한것 반환받음
return li;
}
public void up_date(JBean bean) {
String sql="update spring_table set str1=? where num1=?";
db.update(sql, bean.getStr1(), bean.getNum1());
}
public void de_lete(int n) {
String sql="delete from spring_table where num1=?";
db.update(sql, n);
}
}
6) MapperClass
package co.jw.sol.db;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import co.jw.sol.beans.JBean;
@Component
public class MapperClass implements RowMapper<JBean> {
public JBean mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException{
JBean bean=new JBean();
bean.setNum1(rs.getInt("num1"));
bean.setStr1(rs.getString("str1"));
return bean;
}
}
7) MClass
package co.jw.sol.main;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import co.jw.sol.beans.JBean;
import co.jw.sol.config.BBean;
import co.jw.sol.db.JdbcDAO;
public class MClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx=
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BBean.class);
JdbcDAO dao=ctx.getBean(JdbcDAO.class);
JBean b1=new JBean();
b1.setNum1(1);
b1.setStr1("인성");
dao.in_sert(b1);
JBean b2=new JBean();
b2.setNum1(2);
b2.setStr1("송이");
dao.in_sert(b2);
//dao.de_lete(2);
List<JBean> li=dao.sel_ect();
for(JBean b3:li) {
System.out.println(b3.getNum1());
System.out.println(b3.getStr1());
}
ctx.close();
}
}

[ AOP 개념 ]
- 관점 지향 프로그래밍이란 OOP로 독립적으로 분리하기 어려운 부가 기능을 모듈화하는 방식
- Spring의 핵심 개념 중 하나인 DI가 애플리케이션 모듈들 간의 결합도를 낮춰준다면, AOP는 애플리케이션 전체에 걸쳐 사용되는 기능을 재사용하도록 지원하는 것
- OOP에선 공통된 기능을 재사용하는 방법으로 상속이나 위임을 사용
- 하지만 전체 어플리케이션에서 여기저기에서 사용되는 부가기능들을 상속이나 위임으로 처리하기에는 깔끔하게 모듈화가 어려움
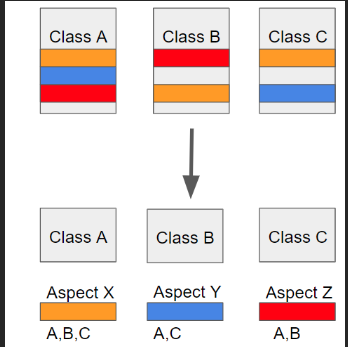
흩어진 관심사 모듈화!! (ex A클래스에서 주황, 파랑, 빨간색 이 하나라도 바뀌면 클래스 B,C다 바꿔줘야함 )=> 방지하기 위해 흩어져 있는 관심사를 모듈화 => 모듈화 시켜놓고 어디에 적용시킬지만 정의해주면 됨 => 모듈화 시켜 놓은 블록 : Aspect
Aspect : 흩어진 관심사를 모듈화 한 것.
Target : Aspect를 적용하는 곳. 클래스, 메서드
Advice : 실질적으로 어떤 일을 해야 할 지에 대한 것, 실질적인 부가기능을 담은 구현체
Join Point : Advice가 적용될 위치 혹은 끼어들 수 있는 시점. 메서드 진입 시점, 생성자 호줄 시점, 필드에서 꺼내올 시점 등 끼어들 시점을 의미. 참고로 스프링에서 Join Point는 언제나 메서드 실행 시점을 의미
before : 비지니스 메소드 실행 전에 Advice 메소드 실행
after-returning : 비지니스 메소드가 성공적으로 리턴되면 Advice 메소드 동작. 즉 비지니스 메소드가 성공적으로 실행되었을 경우에만 Advice 메소드 동작
after-throwing: 비지니스 메소드 실행중 예외가 발생할 경우 Advice 메소드 실행. 즉 비지니스 메소드가 실행에 실패했을 경우에만 Advice 메소드 실행
after : 비지니스 메소드의 성공 실패와 상관없이 비지니스 메소드 실행 후 무조건 Advice 메소드 동작
around : 비지니스 메소드 실행 전과 실행 후 Advice 메소드 동작하는 형태
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver/1.9.19에서 코드 가져올 때 <scope>runtime</scope>
이 부분은 지워주기 => 에러 발생할 수도 있음 !!!
'네이버 클라우드 부트캠프 > 복습 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 54일차 스프링 [ MVC - 추출, 주입, form taglib ] (1) | 2024.05.08 |
|---|---|
| 53일차 스프링 [ MVC ] (0) | 2024.05.07 |
| 51일차 스프링 [ 주입 DI ] (0) | 2024.05.02 |
| 50일차 스프링 [ 환경설정, 개념 ] (0) | 2024.05.01 |
| 46일차 JSP [ 게시판 만들기 ] (0) | 2024.04.25 |





